SeedBlink Blog
all Things Equity
Unlocking Liquidity: Demystifying the Secondary Market for Startup Investments
In recent years, the secondary market for startup investments has emerged as a viable alternative for investors looking to buy or sell ownership stakes in private companies. This article examines how the secondary market for private companies' investments works, the different types of transactions involved, and the various players participating. Whether you are an experienced startup investor or simply curious about the investment landscape, this article provides insights into the rapidly evolving world of the secondary market for early-stage companies.
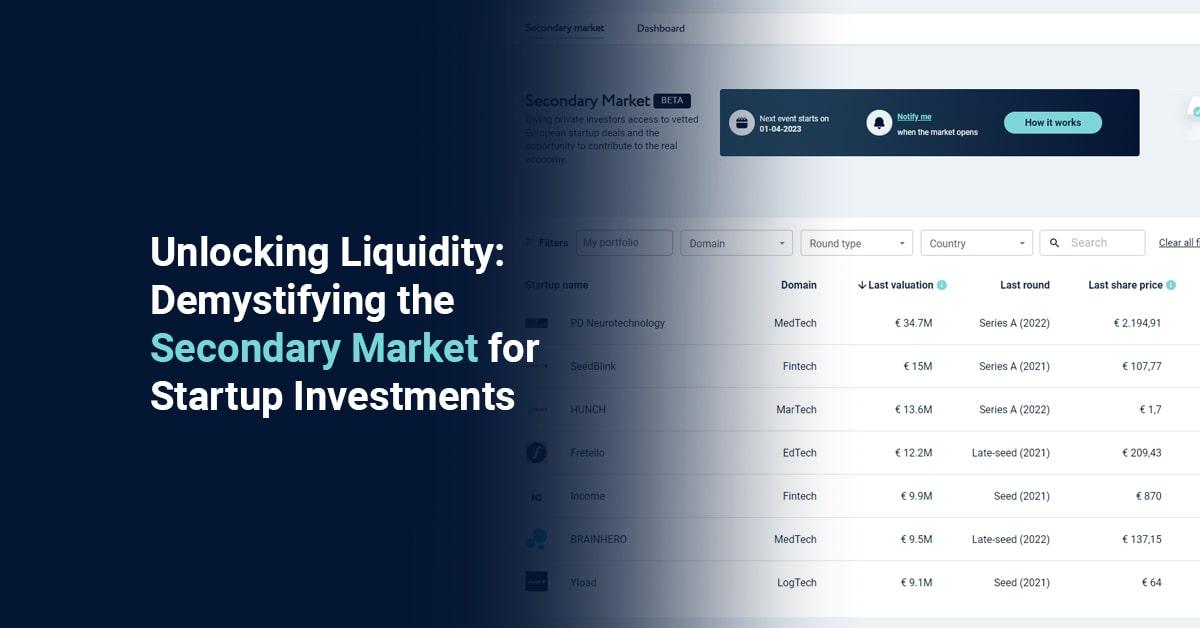
SeedBlink’s Secondary Market is among the first bulletin boards implemented in Europe as per the new European Crowdfunding Service Provider regulation.
Through a secondary market, existing investors can exchange their assets and increase the liquidity of their portfolio investments.
Pitchbook shared that startups stay private longer in the market, making founders and investors eager to transform their assets into cash.
Two pandemic years didn’t impact secondary markets in a significant way. There was a small decrease once COVID-19 started in 2020, but the second half of that year brought a stronger field for secondary markets. The new context brought a greater desire for more liquidities, so this is how the market faced a growing need for secondary transactions where people could trade their shares in exchange for money.
What is a Secondary Market?
A secondary market is a marketplace where private investors buy and sell assets they already own and exist for a wide range of securities, including stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments.
These markets provide liquidity to investors who wish to sell their securities before they reach maturity or before the issuer makes a public offering. Additionally, they allow new investors to enter the market by purchasing existing securities, which can be less expensive than buying newly issued shares.
There are several types of secondary markets, including
- Regular secondary market: A regular secondary market, also known as a secondary market, is a market where previously issued securities are bought and sold among investors. Examples of regular secondary markets include stock exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Nasdaq Stock Market.
- Over-the-counter (OTC) market: An OTC market is decentralized, where securities are traded directly between two parties without a centralized exchange. Examples of OTC markets include the bond market and the foreign exchange market.
- Private equity secondary market: A private equity secondary market is a specialized market where ownership stakes in private companies are bought and sold among investors. Private equity secondary markets allow investors to exit their investments and for new investors to enter the market.
- Real estate secondary market: A secondary market is where real estate assets, such as commercial or residential properties, are bought and sold among investors. Real estate secondary markets provide liquidity to investors wishing to sell their assets before maturity.
- Derivatives market: A derivatives market is a market where financial instruments, such as options and futures contracts, are bought and sold based on the value of an underlying asset, such as a stock or commodity. Derivatives markets allow investors to manage risk and hedge their investments.
- Cryptocurrency secondary market: A cryptocurrency secondary market is a market where cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are bought and sold among investors. Cryptocurrency secondary markets are decentralized and operate 24/7, allowing investors to trade cryptocurrencies anytime.
As we advance through the article, we’ll focus exclusively on how secondary markets can benefit your private equity portfolios, especially startup investments.
Secondary Market in Startup Investments
A secondary market for startup investments refers to a marketplace where private equity investments are bought and sold by investors after the initial offering. In other words, it is a platform where investors can buy and sell their ownership stakes in private companies previously acquired through a primary market during a financing round conducted by the target company.
Startup equity investments are typically illiquid, meaning they cannot be easily bought or sold. The secondary market allows investors to exit their assets before the end of the holding period or acquire additional investments in private companies. Liquidity is not guaranteed through a secondary market.
The secondary market for startup investments can include a variety of buyers and sellers, including institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, and family offices.
Why are secondaries important for your investment strategy?
Secondary Market for Buyers
The secondary market is essential for buyers as it offers several advantages over traditional primary market investments.
Here are some key market roles for a secondary buyer:
- Access to a broader range of investment opportunities: Secondary deals provide buyers access to a wider range of investment opportunities that may not be available in the primary market.
- Reduced time to exit: Buyers in the secondary market can acquire startup equity holdings that have matured or have already passed through their initial growth phase. This reduces the time it takes for buyers to exit their investments.
- Mitigate the negative effects of the J-curve: As a buyer, you can avoid the traditional J-curve, where initially, the capital is being called to finance acquisitions.
- Reduced risk: Buyers in the secondary market can acquire shares through their initial growth phase.
- Flexibility: Secondary investments offer buyers more flexibility than the primary market, as they can choose which specific investments to acquire and negotiate the terms.
Secondary Market for Sellers
The secondary market for private equity provides an important avenue for sellers to liquidate their holdings and realize returns on their investments.
Here are some of the key roles of a secondary market for sellers:
- Access to capital: The sale of private equity holdings in the secondary market could give sellers access to the capital they can use for new investments.
- Portfolio management: Startup investments are often illiquid and difficult to manage within a diversified investment portfolio. The secondary market allows sellers to rebalance their portfolios, make better investment decisions and manage risk more effectively.
- Exit strategy: The secondary market can provide an exit strategy for investors who may have held their investments longer than initially anticipated or are seeking to exit an investment to pursue other opportunities.
- Price discovery: The secondary market can help sellers to determine the market value of their holdings, providing a benchmark against which they can assess the performance of their investments.
Are secondary markets good opportunities for founders and their startups?
Overall, the secondary market for startup investments provides several advantages for founders and startups, such as:
- Access to liquidity.
- Diversification of investors in the fundraising process.
- Increased brand recognition.
Compared to an IPO, selling shares in the secondary market can be less burdensome regarding regulatory compliance, saving time and money.
These factors make it attractive for founders and startups looking to access capital and grow their businesses.
8 elements to know before having your first transaction through a secondary market
1. What is a bulletin board?
Bulletin boards allow secondary investors to post details about the investments they want to buy or sell, including the company's name, industry, investment size, and expected returns.
Similarly, potential buyers can post their investment criteria, indicating the types of companies or sectors they are interested in and the amount they are willing to invest.
The European Crowdfunding regulation regulates bulletin boards in Europe. So, whenever you are interested in acquiring or selling crowdfunding assets through a secondary market, look after platforms authorized by ECSPR (The European Securities and Markets Authority).
2. How does a secondary market event take place?
The process for a secondary market event can vary depending on the size and complexity of the transaction, but here is a general overview of the steps involved:
- You define an offer for one of your portfolio companies from your portfolio and publish it on the bulletin board to reach potential buyers.
- Initial investors will be first notified, and after ten days, the offer will be visible to all verified users on the platform.
- The negotiation process starts, investors accept or decline the purchase price, and once everything is clear, you can sign the agreement.
- On SeedBlink Secondary Market, events take place quarterly for one month.
- After all necessary documents are signed, the transaction is visible within your portfolio.
The timeline of a secondary market event can vary depending on the complexity of the transaction and the level of due diligence required. Smaller and simpler transactions may take a few weeks, while more extensive and more complex transactions can take several months.
3. Importance of liquidity for your investment strategy.
Liquidity is critical when constructing an investment portfolio, as it impacts an investor's ability to manage their investments effectively. Sufficient liquidity in an investment portfolio is essential to meet short-term cash flow needs or exploit potential investment opportunities.
Additionally, liquidity helps diversify an investment portfolio, offering private equity investors an allocation of funds across different asset classes, sectors, and geographies.
4. Liquidity is not guaranteed in the secondary market.
While the secondary market for startup investments offers greater liquidity than the primary market, it is still less liquid than public markets. This is because this type of market is decentralized and fragmented, which means there is no centralized exchange for these transactions.
As a result, liquidity in the secondary market for startup investments is not guaranteed. The availability of buyers and sellers can vary depending on market conditions, and there may be limited demand for a particular investment at a given time. This can make it difficult for investors to sell their holdings promptly, particularly if they need to raise cash quickly.
5. Secondary markets are safe & secure.
Security is a critical aspect of any financial transaction, and secondary market transactions are no exception. To ensure the security of these transactions, they are often conducted through a network of regulated intermediaries who provide custody services and help facilitate the transaction.
Confidentiality is another key consideration in secondary market transactions. Investors are typically required to sign non-disclosure agreements to ensure that sensitive information about the asset management, such as financial information or business plans, is kept confidential.
Additionally, the parties involved in the transaction, such as the buyer and seller, must provide proof of identity and undergo background checks to ensure that they are legitimate counterparties and minimize the risk of fraud.
6. Price per share before and after a secondary sale.
The price per share of startup assets can change before and after a secondary market transaction depending on various factors such as market conditions, the performance of the underlying assets, and the level of demand from buyers.
Also, the seller can use an indicative price given by the last financing round when making an offer. Indicative prices in the secondary market refer to the nominal value of a share (the last commercial value established in the previous equity fundraising event). In contrast, the asking price is arbitrary. This can be lower, equal, or higher than the indicative price and represents the starting point of the negotiation process.
7. Startup investments are still risky.
The success of a secondary market event and its transaction volume also depends on the company’s performance.
This is because the value of a startup investment is primarily based on the company's future potential, which is influenced by factors such as market conditions, competition, and management decisions.
For example, suppose a startup is performing well and meeting its growth targets. In that case, the value of its equity may increase, making it more attractive to potential buyers in the secondary market. Conversely, if a startup is experiencing financial difficulties or fails to meet its growth targets, the value of its equity may decrease, making it more difficult to find buyers in the secondary market.
8. Less hustle with paperwork.
Secondary market transactions typically involve just some legal documents or paperwork. The transaction platform usually handles this.
However, when in doubt, buyers and sellers need to seek the advice of legal and financial professionals to ensure that all necessary paperwork and legal documents are in order and that the transaction complies with all applicable laws and regulations.
Primary Market vs. Secondary Market
The primary and secondary markets are essential to the private equity market.
The primary market refers to investing directly from the issuer, typically a company, a private equity fund, or a fund of funds. This involves investing in the company or fund in exchange for equity or ownership stake, expecting a return on the investment over a specific time.
Conversely, the secondary market refers to buying and selling existing private startup investments between investors.
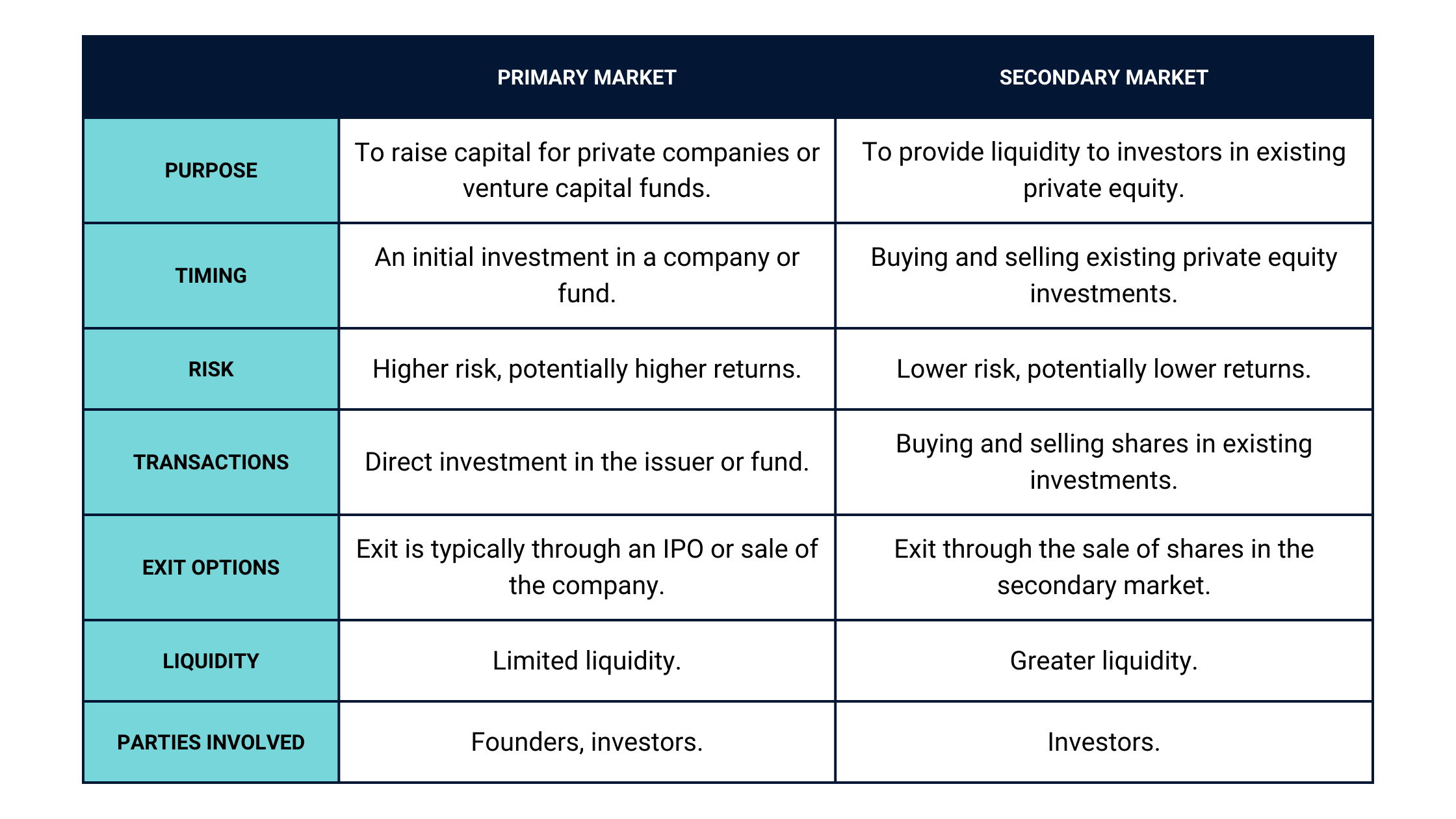
Primary market
As a startup founder, when addressing investors for a possible funding round, you offer a package of assets from your company. These assets have multiple forms depending on investors' needs, whether debt-based or in the form of equity and bonds issued as stocks or shares.
Secondary market
If transactions happen between startups and investors in primary markets, in the secondary market, the exchange of assets occurs only between investors. In a case of a secondary market event between investors, part of a venture capital fund, general partners, and limited partners can play different roles.
Asset owners trading their assets in the secondary market are the only ones gaining profits from the transaction. The company doesn’t receive anything in return.
Join our newsletter
Your go-to source for European startup news, equity trends, VC insights, and investment opportunities.